Hello World from OSS Silicon Valley
HowToUse/Git/1.7
_ Install&Setup
_ Install Git from Cygwin
(TBD)
_ Configuration
Step.1) Setup configuration as needed.
Example)
$ git config --global color.ui true $ git config --global user.name "<User Name>" $ git config --global user.email "<Email address>" $ git config --global core.editor <Editor> $ git config --global alias.mylog "log --pretty=format:'%h %s [%an]' --graph"
Step.2) Setup .ignore as needed.
Example)
logs/*.log
_ HowToUse
_ General Operation
- Step.1
- Clone the repository
$ git clone <Remote Repository>
- Step.2
- Create a new branch.
$ git checkout -b <Branch Name>
- Step.3
- Edit files.
- Step.4
- Stage updated files.
$ git add .
You can reset the updated files.
$ git reset HEAD
- Step.5
- Commit the files.
$ git commit -m "<commit message>"
If you are using GitHub, you can close the issue with the following commit message.
$ git commit -m "Close #<issue no>"
- Step.6
- Merge the commited files into master.
$ git checkout master $ git merge <Branch Name>
- Step.7
- Remove the branch.
$ git branch -d <Branch Name>
- Step.8
- Push the files to remote server.
$ git push
_ Setup Repository server
_ Original Git Server
Refer HowToUse/Git Daemon/1.7
_ GitHub
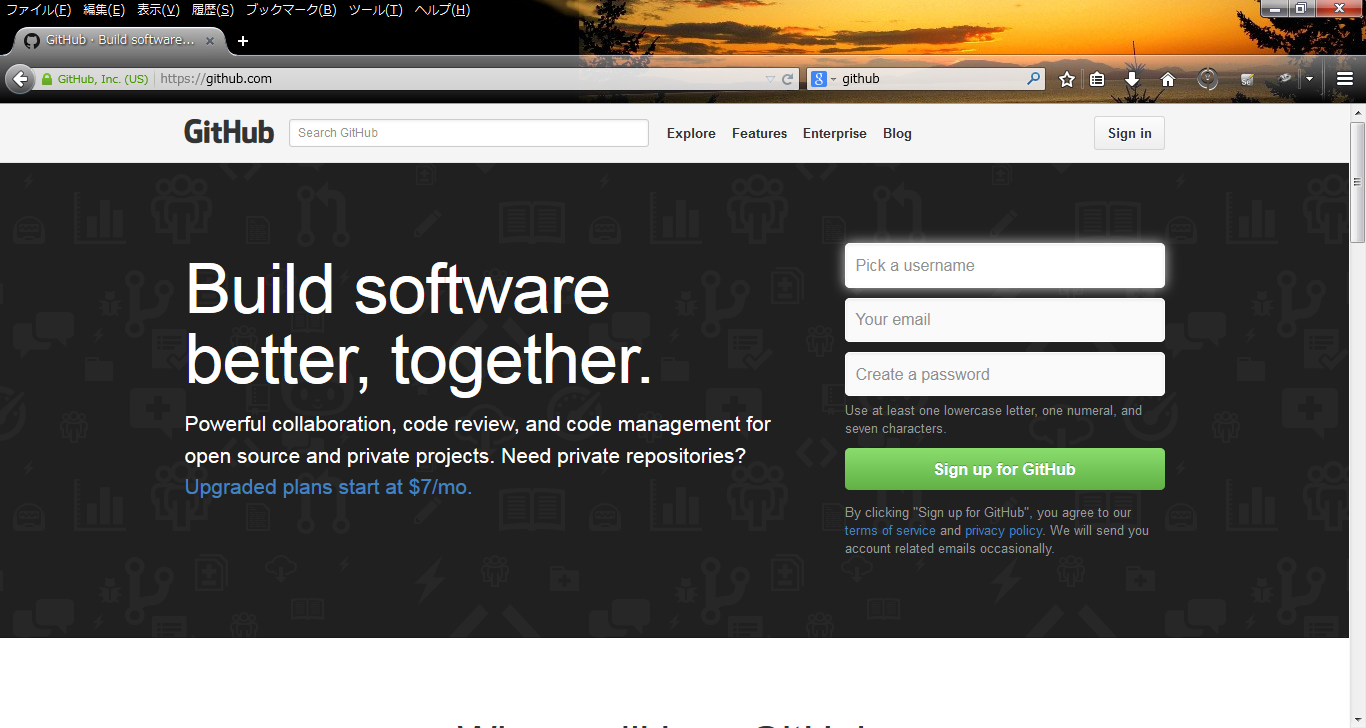
- Step.1
- Access the GitHub web site and sign up(https://github.com/).
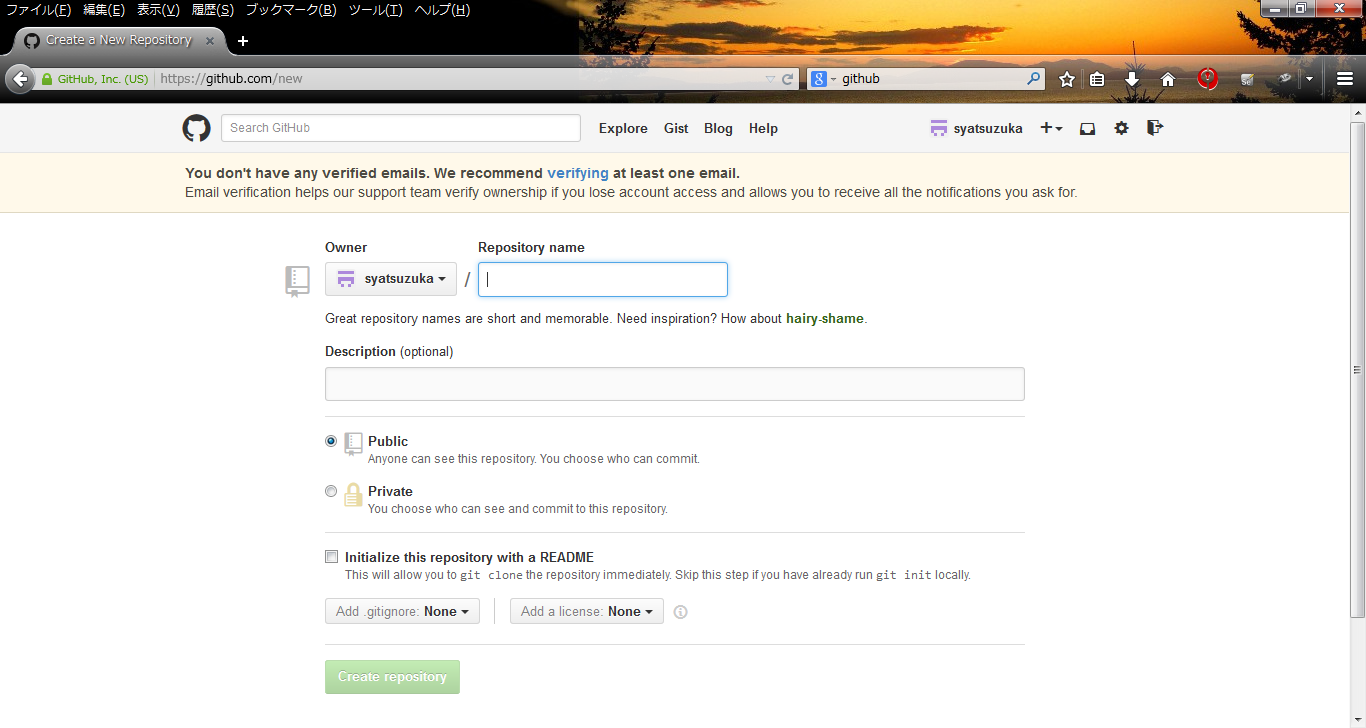
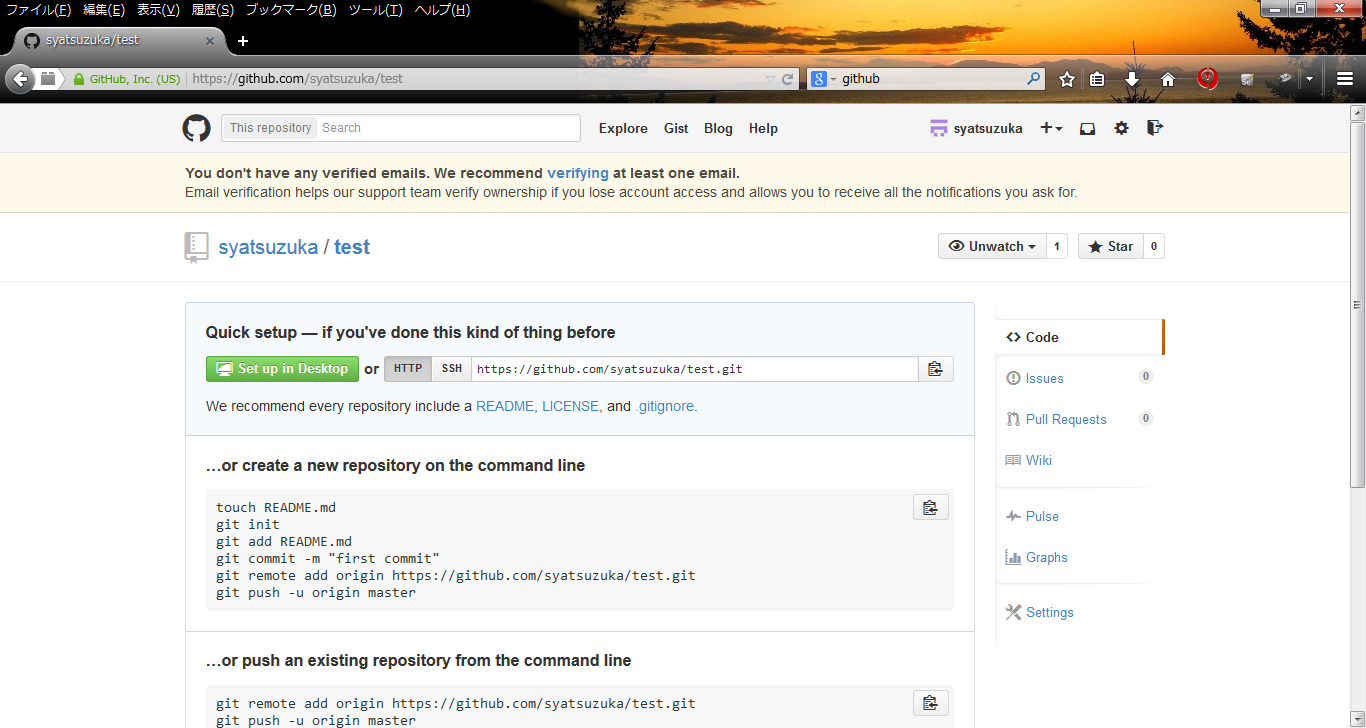
- Step.2
- Click "create" button and create new repository.
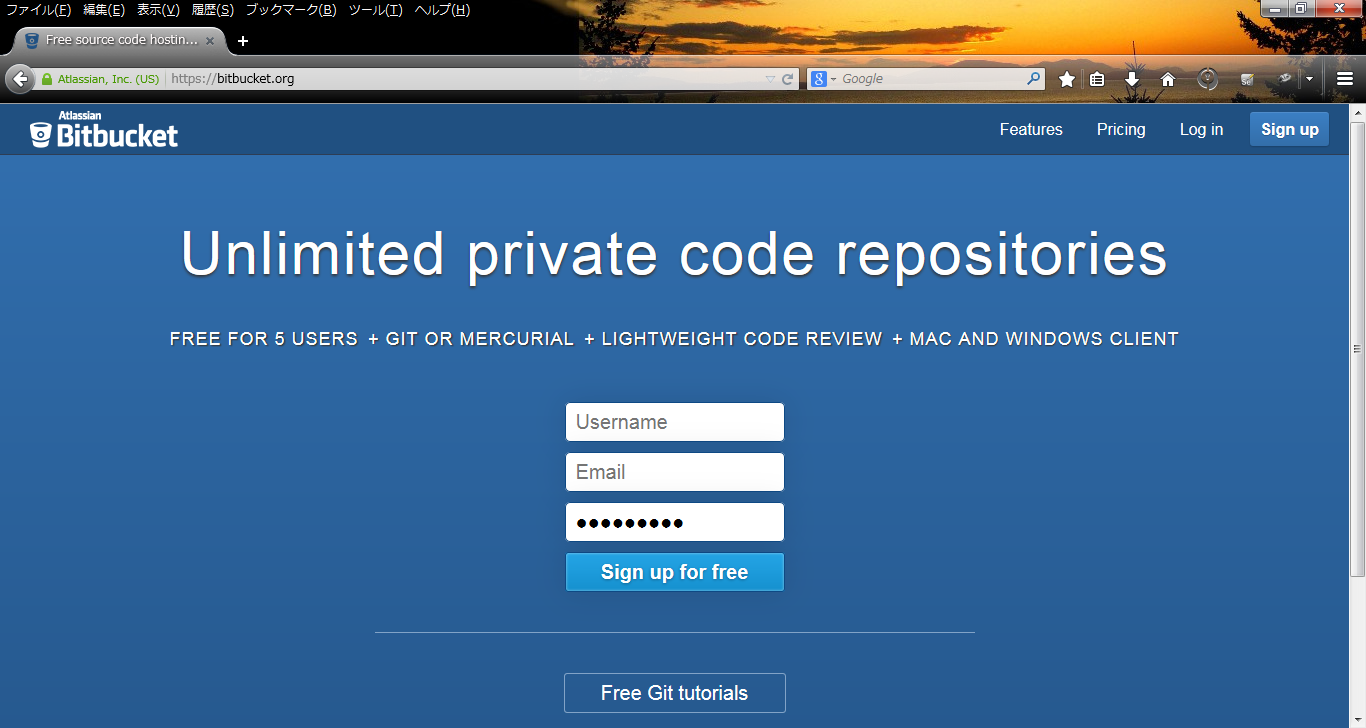
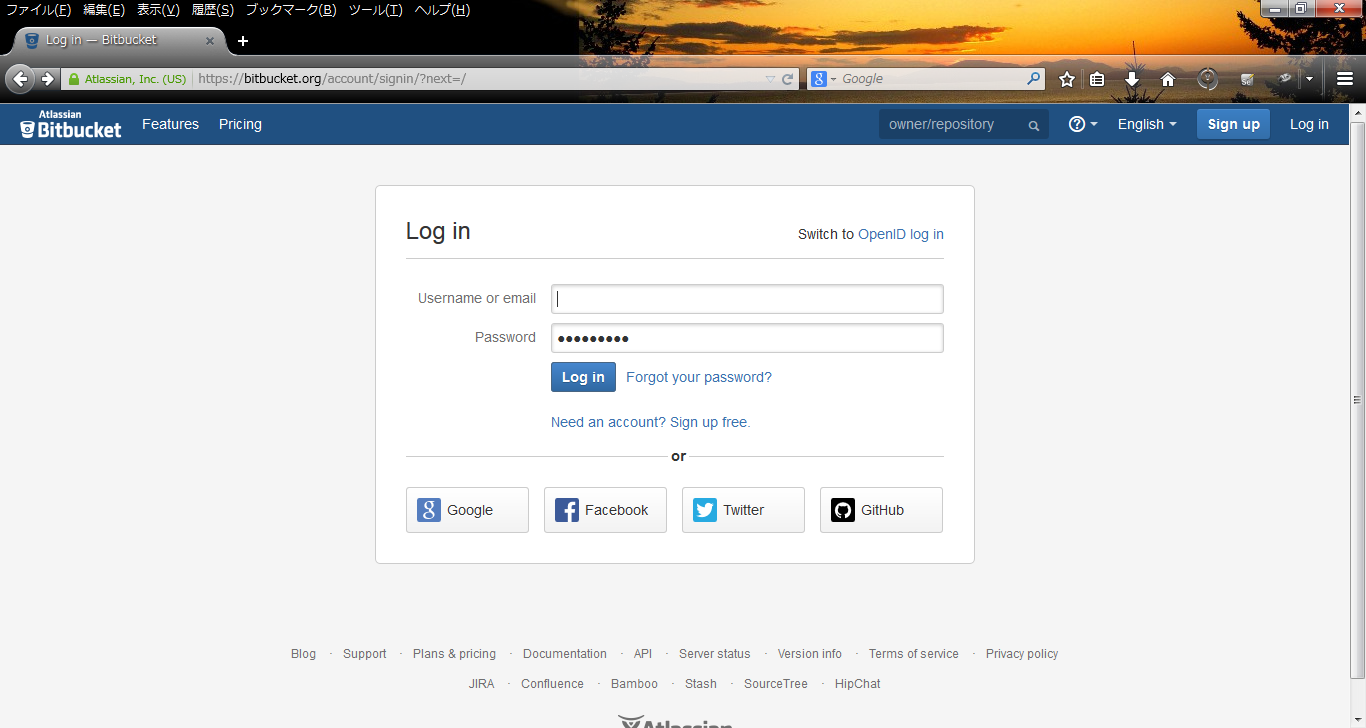
_ BitBucket
- Step.1
- Access the BitBucket web site and sign up(https://bitbucket.org/).
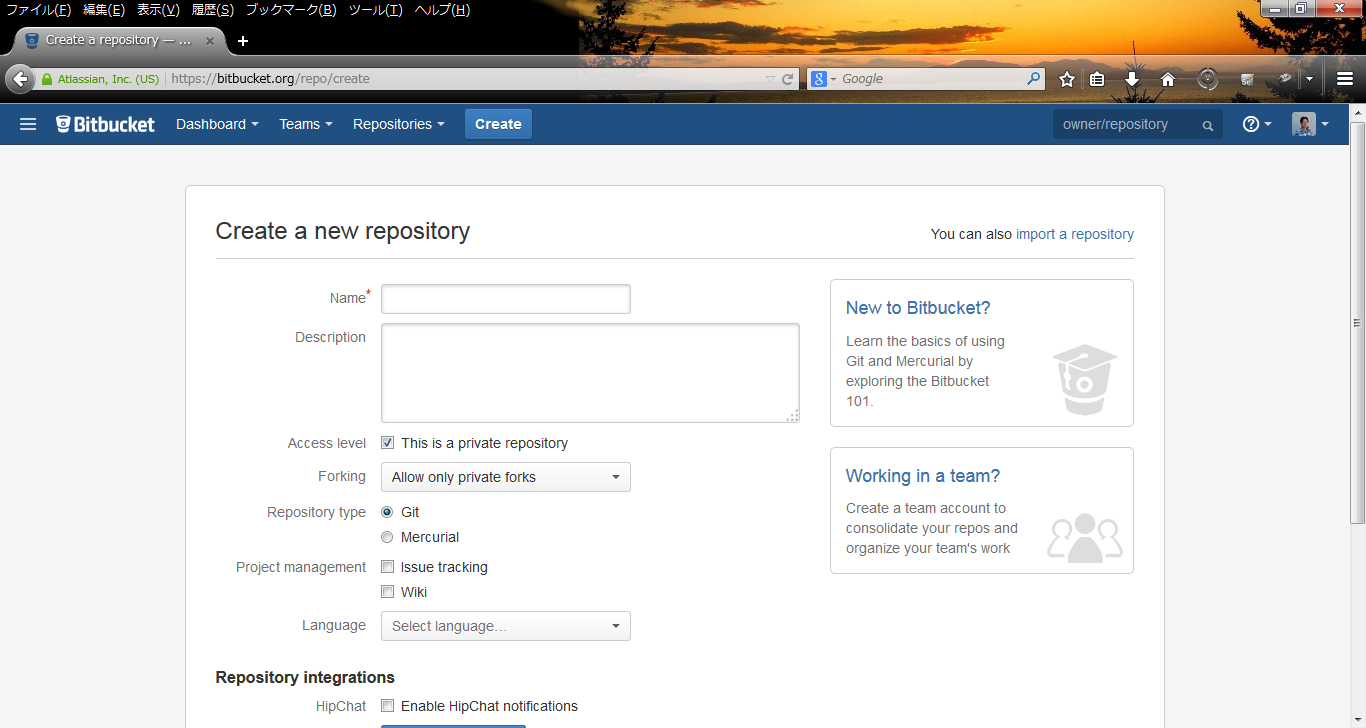
- Step.2
- Click "create" button and create new repository.
_ Create Repository
_ Original Git Server
- Step.1
- Create your local repository.
# mkdir <Local Repository> # cd <Local Repository> # git init # git remote add origin <User Name>@<Host name>:<Repository Path>
(Example)
# git remote add origin syatsuzuka@192.168.56.101:/home/syatsuzuka/repo/test.git
- Step.2
- Check in the first file.
# touch readme.txt # git add readme.txt # git commit -m 'Initial commit' # git push -u origin master
_ GitHub
- Step.1
- Create your local repository.
# mkdir <Local Repository> # cd <Locak Repository> # git init # git remote add origin https://<User Name>@github.com/<User Name>/<Repository Name>.git
(Example)
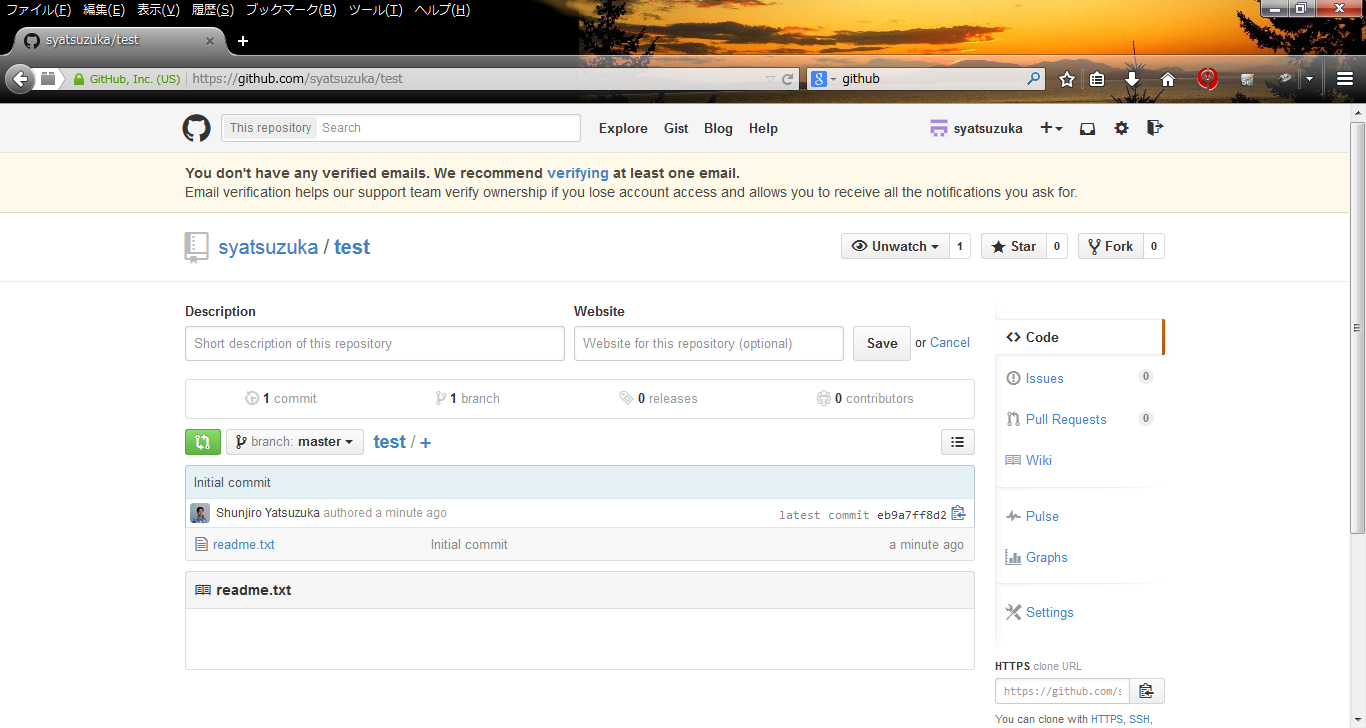
# git remote add origin https://github.com/syatsuzuka/test.git
- Step.2
- Check in the first file.
# touch readme.txt # git add readme.txt # git commit -m 'Initial commit' # git push -u origin master
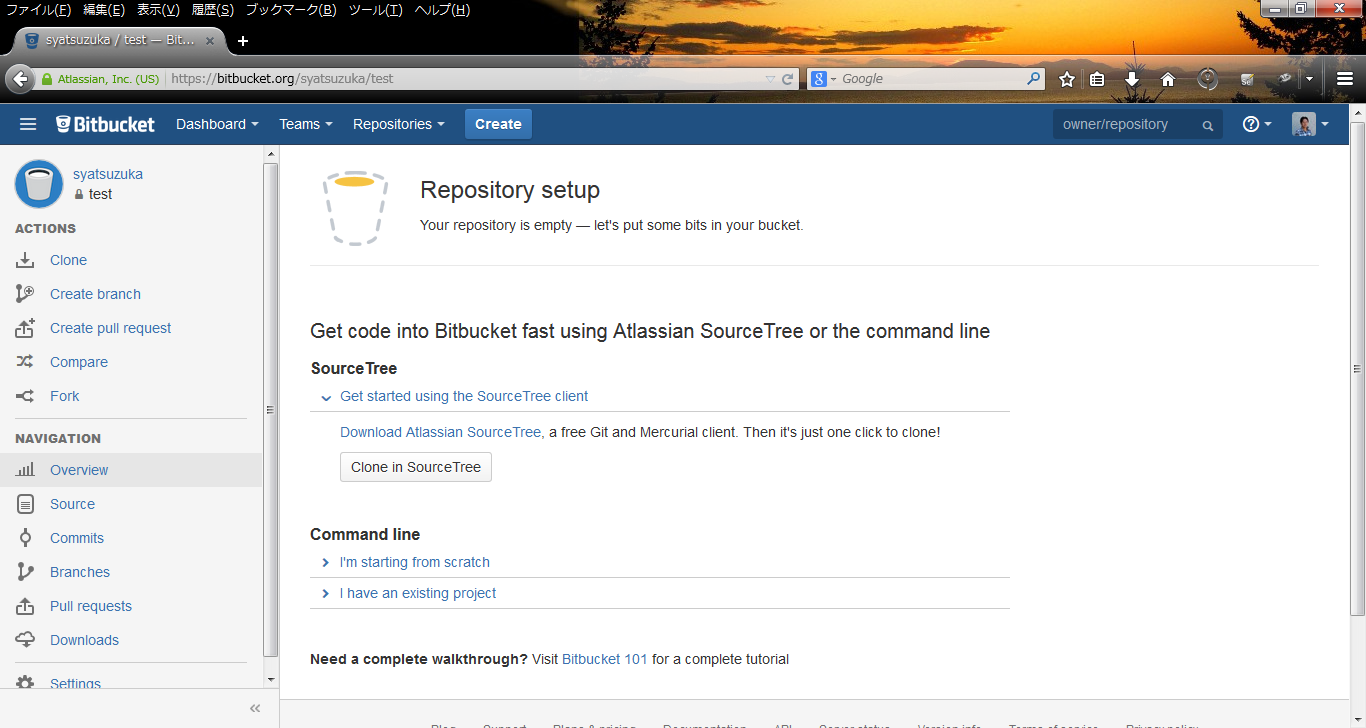
_ BitBucket
- Step.1
- Create your local repository.
# mkdir <Local Repository> # cd <Locak Repository> # git init # git remote add origin https://<User Name>@bitbucket.org/<User Name>/<Repository Name>.git
(Example)
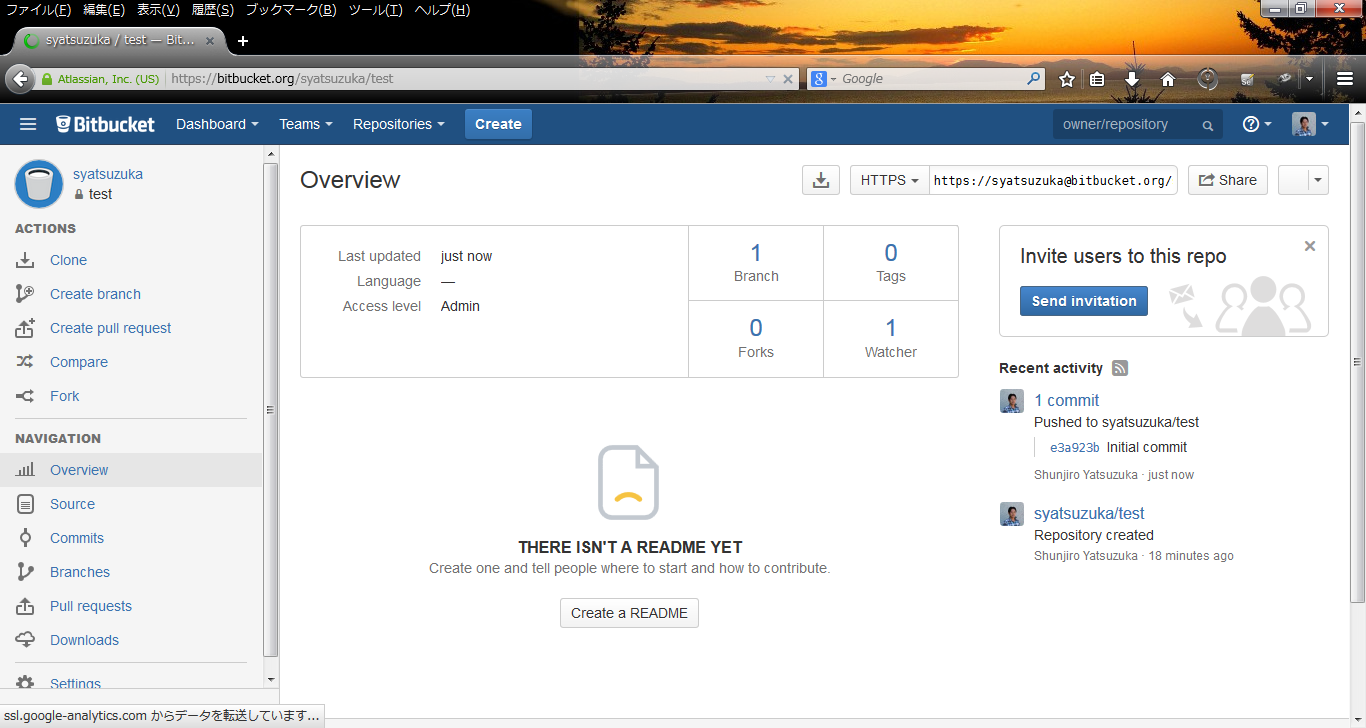
# git remote add origin https://syatsuzuka@bitbucket.org/syatsuzuka/test.git
- Step.2
- Check in the first file.
# touch readme.txt # git add readme.txt # git commit -m 'Initial commit' # git push -u origin master
_ Maintain files
_ Comand Line
- Step.1
- Clone the existing repository to local
$ git pull <Repository Path>
- Step.2
- Edit and check in the files to local repository
(edit files) $ git add . $ git commit -m '<message>'
- Step.3
- Push the updated file to remote repository
# git tag -a <version> -m '<description>' # git pull origin # git push origin
When you encounter "Fatal Error" to upload files to GitHub, you may be able to deal with the following operations.
$ git remote set-url origin https://<your github account>@<your github repository path>
(Example)
$ git remote set-url origin https://syatsuzuka@github.com/nasebanal/co-working.git
$ unset SSH_ASKPASS $ git push origin
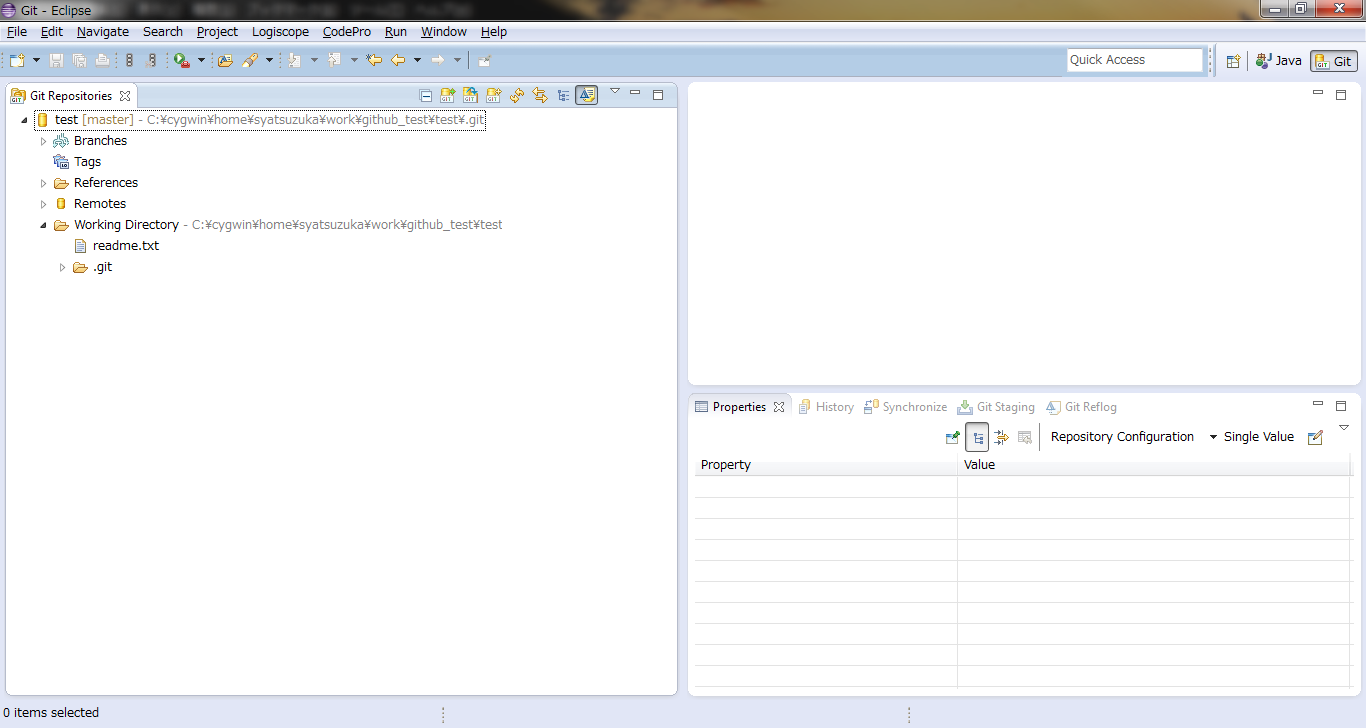
_ Eclipse
- Step.1
- Clone the remote repository.
# git clone <Repository Path>
(Example)
# git clone https://syatsuzuka@bitbucket.org/syatsuzuka/test.git
- Step.2
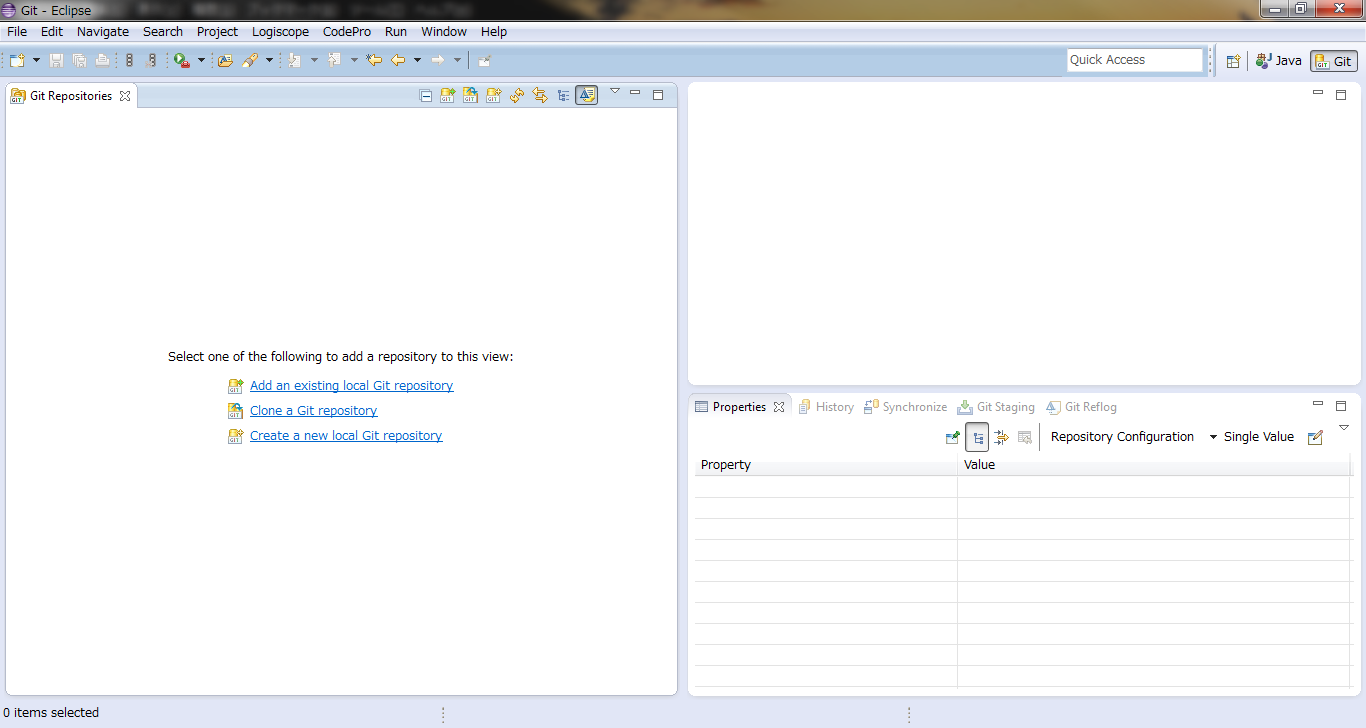
- Launch Eclipse and switch to Git Perspective.
- Step.3
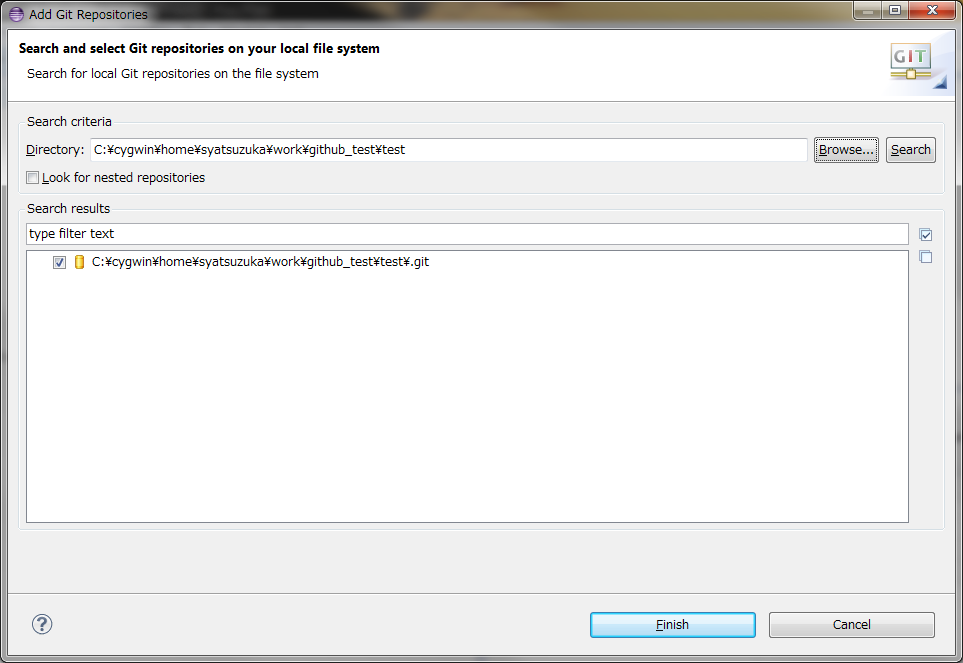
- Click "Add an existing local Git repository" and setup Local Repository Path.
- Step.4
- Edit the files.
- Step.5
- Commit and push the modified files. Eclipse Plugin sometimes doesn't have full functionalities for the external utilities such as maven or git, so I recommend you to use command line for fundamental operations except for editing files.
_ Other operations
_ Maintain submodule
- Step.1
- Get submodule in the workspace.
# git submodule <repository path> <submodule directory>
Then you can include submodules to your project without maintaining version control for its submodule code.
_ Author
S.Yatsuzuka
Attach file:  GitHub_fig5.png 195 download
[Information]
GitHub_fig5.png 195 download
[Information]
 GitHub_fig4.png 203 download
[Information]
GitHub_fig4.png 203 download
[Information]
 MaintainFiles_fig1.png 175 download
[Information]
MaintainFiles_fig1.png 175 download
[Information]
 MaintainFiles_fig2.png 178 download
[Information]
MaintainFiles_fig2.png 178 download
[Information]
 MaintainFiles_fig3.png 178 download
[Information]
MaintainFiles_fig3.png 178 download
[Information]
 BitBucket_fig5.png 171 download
[Information]
BitBucket_fig5.png 171 download
[Information]
 BitBucket_fig3.png 203 download
[Information]
BitBucket_fig3.png 203 download
[Information]
 GitHub_fig2.png 178 download
[Information]
GitHub_fig2.png 178 download
[Information]
 GitHub_fig1.png 206 download
[Information]
GitHub_fig1.png 206 download
[Information]
 GitHub_fig3.png 188 download
[Information]
GitHub_fig3.png 188 download
[Information]
 BitBucket_fig4.png 180 download
[Information]
BitBucket_fig4.png 180 download
[Information]
 BitBucket_fig2.png 190 download
[Information]
BitBucket_fig2.png 190 download
[Information]
 BitBucket_fig1.png 200 download
[Information]
BitBucket_fig1.png 200 download
[Information]
Last-modified: 2016-11-06 (Sun) 07:51:25 (2728d)